The Unseen Burden: Understanding Calcific Tendinopathy
Calcific tendinopathy often goes beyond just shoulder pain, significantly impacting your daily activities. With deposits primarily in the supraspinatus tendon in 80% of cases, the resulting inflammation can sharply limit your shoulder movement, making tasks like dressing or reaching overhead difficult. Between 10 to 20% of sufferers experience bilateral calcifications, increasing the functional impairment. Women in their 40s and 50s are disproportionately affected, accounting for 70% of cases. This silent buildup of calcium within your tendons gradually reduces shoulder flexibility and induces pain, often striking suddenly without obvious injury, disrupting both work and leisure.
The Anatomy of Pain: Causes Behind Calcific Tendinopathy
Calcific tendinopathy arises from abnormal calcium deposits that develop within the tendons of your rotator cuff, triggering inflammation and intense pain. These deposits most often affect the supraspinatus tendon, disrupting its normal function and causing stiffness. The buildup creates pressure within the tendon structure and irritates surrounding tissues, leading to the sharp pain and limited movement you may experience. Understanding these changes helps explain why your shoulder feels sore and why targeting the calcifications directly is key to effective treatment.
Cell Transformation and Calcium Production
Your tendon cells, known as tenocytes, can undergo an unusual transformation into chondrocytes, the type of cells responsible for producing cartilage. This shift initiates the inappropriate formation of calcium deposits within the tendon. Essentially, your tendon starts developing bone-like material, disrupting its flexibility and causing pain. This cell transformation is a primary driver behind the pathology of calcific tendinopathy and helps explain how calcium deposits form without direct injury.
Demographic Insights and Risk Factors
Calcific tendinopathy is most commonly seen in individuals in their 40s and 50s, with a female to male ratio of approximately 70% to 30%. Women are more likely to develop this condition, possibly due to hormonal influences or differences in tendon biology. Additionally, between 10 to 20% of sufferers show calcifications in both shoulders, indicating bilateral involvement is not uncommon. The supraspinatus tendon is affected in 80% of cases, followed by the infraspinatus (15%) and subscapularis (5%).
- Primarily affects individuals in their 4th and 5th decades of life
- Women constitute around 70% of cases
- Bilateral shoulder involvement occurs in up to 20% of patients
- Predominant localisation in the supraspinatus tendon (80%)
- The infraspinatus and subscapularis tendons are less commonly affected
Diving deeper into risk factors, repetitive shoulder movements or overuse, particularly in occupations or sports involving overhead activity, can increase your susceptibility. A history of metabolic conditions such as diabetes or thyroid disorders has also been linked to higher incidence rates. Genetic predisposition may play a role too, with some families showing increased prevalence of calcium deposits in tendon tissues. The presence of these risk factors can influence the severity and progression of your symptoms and guide your treatment planning.
- Repetitive overhead or strenuous shoulder activity enhances risk
- Underlying metabolic conditions may predispose to calcification
- Genetic factors could contribute to tendency for calcium deposits
- The combination of lifestyle and biological factors shapes the clinical picture
Shockwave Therapy: A Breakthrough in Non-Invasive Treatment
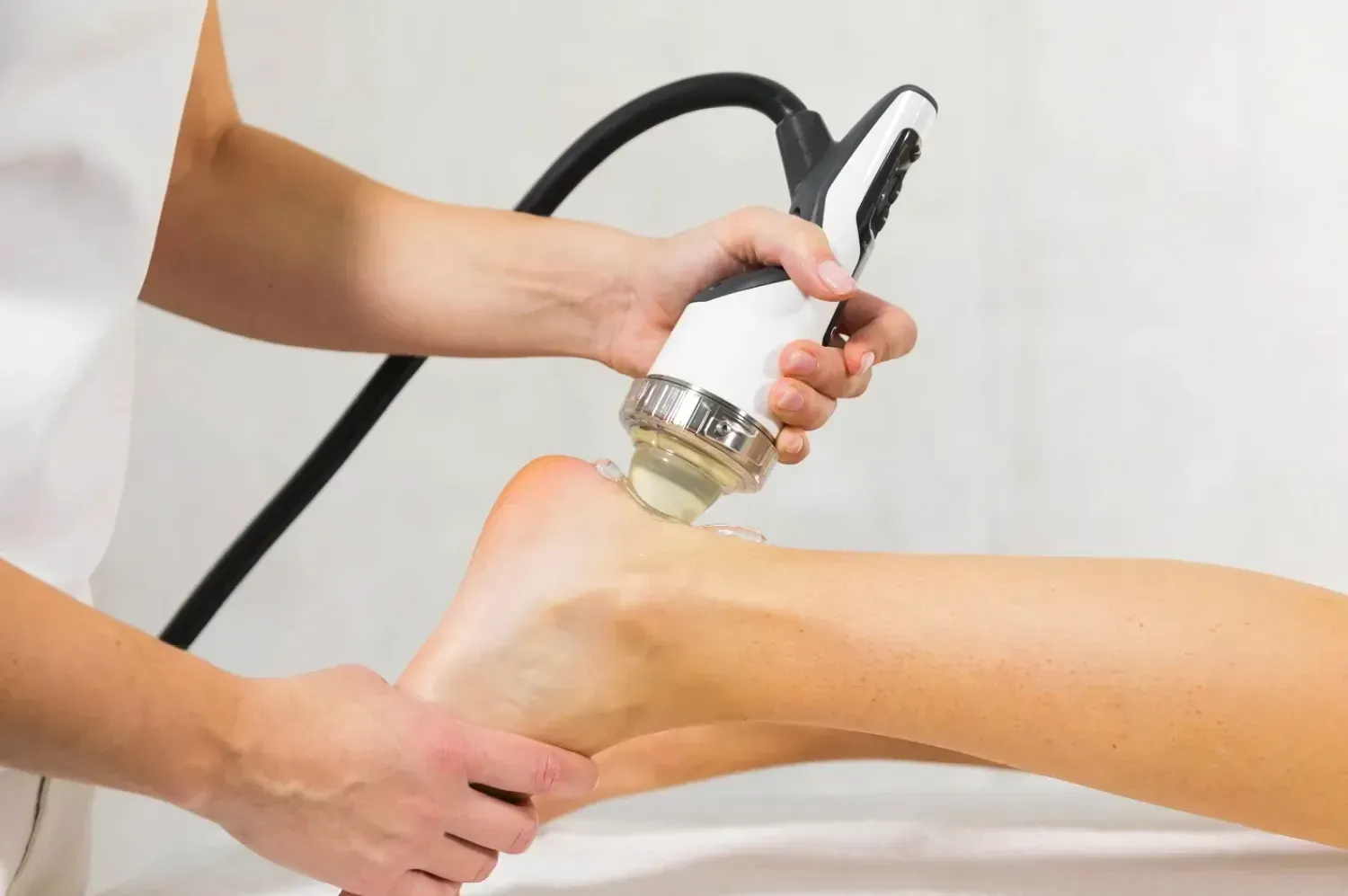
Shockwave therapy offers a cutting-edge, non-invasive solution to managing calcific tendinopathy, targeting the root causes of pain without surgery. By delivering controlled sound waves directly to the affected tendon, it induces healing responses that gradually break down calcium deposits while reducing discomfort. Clinical studies report success rates nearing 90% in pain relief and improved shoulder function, making it a reliable first-line treatment option that supports your recovery while minimising downtime and risks associated with more invasive procedures.
Mechanics of Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy utilises high-energy acoustic pulses that penetrate the soft tissue and calcific deposits in your shoulder tendons. These focused shockwaves generate microtrauma on a cellular level, stimulating blood flow and encouraging tissue regeneration. This mechanical action helps fragment calcium deposits and enhances cellular metabolism within the tendon, setting the stage for accelerated repair without the need for incisions or medication.
How It Triggers the Body’s Healing Process
The microtrauma produced by shockwaves activates your body’s innate healing mechanisms, prompting an influx of growth factors and stem cells to the damaged tendon. This accelerates tissue regeneration and remodels the tendon matrix, while also dampening nerve sensitivity around the area, which reduces pain and discomfort.
Further to the initial physical impact, shockwave therapy stimulates angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels—around the calcific deposits, thereby improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to impaired tissues. Studies have shown increased expression of growth factors such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) post-treatment, which play vital roles in tissue repair. This enhanced microcirculation contributes to both the breakdown of calcium deposits and restoration of tendon elasticity, allowing you to regain movement and reduce symptoms more effectively.
Proven Efficacy: Evidence Supporting Shockwave Therapy
Clinical evidence firmly supports shockwave therapy as an effective treatment for calcific tendinopathy. With success rates reaching nearly 90% for pain reduction and functional improvement, this non-invasive option offers a safe alternative to surgery. Multiple studies highlight its ability to fragment calcium deposits and stimulate healing, making it a dependable choice that you can consider when seeking relief from shoulder pain and stiffness.
Clinical Studies and Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews by Schmitz et al. (2015) and Huisstede et al. (2011) consolidate findings from numerous trials confirming shockwave therapy’s efficacy in treating calcific tendinopathy. Schmitz’s review reported an 88.5% success rate in symptom improvement, with no serious adverse effects documented. Meanwhile, Pakos et al. (2018) demonstrated enhanced outcomes when shockwave was combined with ultrasound-guided needling, reinforcing the value of this approach for targeted treatment.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Treatments
Comparisons between shockwave therapy and other treatment modalities illustrate its advantages in safety, effectiveness, and recovery time. Unlike corticosteroid injections or surgery, shockwave therapy avoids systemic side effects and lengthy rehabilitation. It also offers a less invasive approach with faster symptom relief compared to physiotherapy alone or conservative management. This makes it a preferred first-line treatment for many patients seeking a balance between efficacy and minimal risk.
Comparative Analysis Overview Treatment Option Key Benefits and Considerations Shockwave Therapy Non-invasive, high success rates (~88.5%), stimulates natural healing, minimal side effects, outpatient procedure Corticosteroid Injection Rapid pain relief but potential systemic effects, risk of tendon weakening with repeated use Ultrasound-Guided Needling + Shockwave Enhanced calcium fragmentation, increased treatment precision, improved outcomes over shockwave alone Physiotherapy Alone Supports gradual recovery but often slower symptom resolution, less effective in calcium deposit removal Surgical Intervention Reserved for refractory cases, invasive with longer recovery, higher risk of complications Understanding these distinctions can help you weigh your options better. Shockwave therapy’s combination of safety and efficacy often makes it the optimal initial treatment, while complementary techniques like needling can be considered to enhance results. Consulting your physiotherapist will ensure a tailored plan matching your specific condition and recovery goals.
Treatment Protocols: What to Expect from Shockwave Sessions
Your shockwave therapy sessions will typically involve focused application of sound waves directly to the calcific deposits in your rotator cuff tendons. Expect some discomfort during treatment as the energy targets the calcium build-up. Most patients notice gradual improvements in pain and mobility over the course of multiple sessions. Treatment plans leverage ultrasound imaging to localise deposits precisely, ensuring that shockwaves hit the affected areas efficiently. Close monitoring of your response allows adjustment of intensity and session count to maximise benefit while managing any discomfort.
Recommended Session Frequency and Duration
Three shockwave sessions spaced one week apart form the standard initial protocol, delivering enough treatment for noticeable symptom relief. Depending on how your body responds, this may extend to six sessions to enhance calcium fragmentation and healing. Each session lasts roughly 15 to 20 minutes, striking a balance between effective dosage and tolerability. Higher shockwave intensities tend to yield better outcomes, so your therapist will calibrate the dose to the highest level you can comfortably withstand.
Complementary Approaches for Optimal Recovery
Shockwave therapy works best alongside a tailored physiotherapy rehabilitation programme, focusing on progressive loading and strengthening of the shoulder muscles. Combining treatments with ultrasound-guided needling or corticosteroid injections can accelerate calcific deposit resolution and reduce inflammation. Your therapist may recommend specific exercises targeting scapular stability and rotator cuff endurance to support tendon healing and restore function.
Integrating rehabilitation exercises reinforces the mechanical environment around your shoulder, preventing recurrence and improving range of motion. Ultrasound-guided needling techniques mechanically disrupt calcific deposits while promoting reabsorption, especially when combined with shockwave therapy as shown in Pakos et al (2018). Corticosteroid injections manage acute inflammation but are best used judiciously alongside physical therapy to avoid weakening tendons. Together, these complementary strategies enhance overall recovery and help ensure lasting relief from calcific tendinopathy symptoms.
Diagnostic Essentials: Why Ultrasound is Key Before Treatment
Ultrasound plays a pivotal role in planning your shockwave therapy by providing a clear image of calcific deposits within the rotator cuff tendons. Unlike MRI, ultrasound reveals not just the presence but also the precise size, shape, and location of calcium deposits, enabling targeted treatment. At Complete Physio, you can benefit from this diagnostic tool at no extra cost, ensuring your therapy focuses exactly where you need it for optimal results.
Identifying Calcific Deposits
Ultrasound identifies calcific deposits by producing real-time images that highlight hyperechoic (bright) areas with acoustic shadowing, characteristic of calcium build-up. This detailed visualisation allows your physiotherapist to differentiate between small and large deposits, detect multiple spots, and assess tendon integrity. Understanding these factors helps tailor the approach and predict the potential response to shockwave therapy.
Tailoring Shockwave Therapy to Individual Needs
Your treatment plan adapts according to the ultrasound findings, considering the deposit’s size, hardness, and location. Parameters such as energy flux density, number of pulses, and session frequency are adjusted to ensure the highest tolerated dose is delivered effectively, maximising tissue response while minimising discomfort.
Personalising shockwave therapy enhances its effectiveness by aligning the treatment dose and focus with the specific characteristics of your calcific deposits. For example, larger or denser deposits might require higher energy levels or additional sessions, whereas smaller deposits respond well to moderate dosing. Ultrasound guidance also allows real-time adjustments during treatment, improving precision and outcomes. This customised approach, supported by research demonstrating success rates over 88%, ensures your therapy dynamically addresses your unique pathology rather than following a one-size-fits-all regimen.